Colors play a significant role in our daily lives, influencing our perceptions, emotions, and behaviors in profound ways. The field of color psychology explores how different hues evoke specific psychological responses and impact various aspects of human experience. This article delves into the psychology of color, examining the effects of different colors on emotions, behavior, and cognitive processes.
1. Understanding Color Psychology
Color psychology studies how colors influence human perception and behavior:
- Cultural Significance: Colors can carry cultural meanings and symbolism that influence their psychological impact.
- Personal Associations: Individual experiences and associations with colors can shape emotional responses.
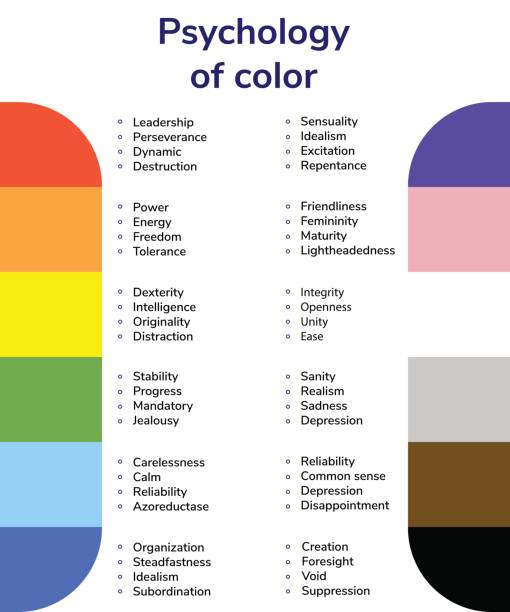
2. Impact of Warm Colors
Warm colors like red, orange, and yellow evoke energetic and stimulating responses:
- Red: Associated with passion, energy, and excitement; can also stimulate appetite and increase heart rate.
- Orange: Evokes enthusiasm, creativity, and warmth; often used to draw attention and create a welcoming atmosphere.
- Yellow: Symbolizes optimism, happiness, and clarity; can enhance concentration and mental agility.
3. Effect of Cool Colors
Cool colors such as blue, green, and purple elicit calming and soothing responses:
- Blue: Promotes calmness, serenity, and productivity; often used to reduce stress and create a sense of stability.
- Green: Symbolizes nature, growth, and harmony; promotes relaxation and is associated with feelings of balance and renewal.
- Purple: Represents luxury, creativity, and spirituality; can evoke a sense of mystery and introspection.
4. Psychological Responses to Neutral Colors
Neutral colors like white, gray, and brown convey simplicity and balance:
- White: Symbolizes purity, cleanliness, and innocence; creates a sense of spaciousness and simplicity.
- Gray: Represents neutrality, stability, and composure; often used as a backdrop to enhance other colors.
- Brown: Evokes warmth, reliability, and earthiness; creates a sense of comfort and groundedness.
5. Cognitive and Behavioral Effects
Colors influence cognitive processes and decision-making:
- Attention and Focus: Bright colors can capture attention and enhance focus, making them effective for signage and visual communication.
- Memory and Recall: Color-coded information can improve memory retention and facilitate information recall.
- Decision-making: Color preferences may influence consumer behavior and purchasing decisions in marketing and branding.
6. Application in Design and Environment
Color psychology informs design choices in various environments:
- Interior Design: Uses colors strategically to evoke desired emotional responses and create specific atmospheres.
- Marketing and Branding: Brands use colors to convey messages, evoke emotions, and establish brand identity and recognition.
- Healthcare and Healing: Hospitals and healthcare facilities use calming colors to promote patient comfort and relaxation.

7. Cross-cultural Considerations
Colors may have different meanings and associations across cultures:
- Symbolism: Red symbolizes luck and prosperity in Chinese culture but may signify danger in Western cultures.
- Cultural Context: Understanding cultural preferences and taboos helps in designing culturally sensitive environments and communications.
8. Personal Preferences and Individual Differences
Individuals may have unique responses to colors based on personal experiences and preferences:
- Color Therapy: Some therapies utilize color to promote emotional healing and well-being, although empirical evidence varies.
- Gender Differences: Research suggests gender differences in color preferences, influencing product design and marketing strategies.
9. Psychological Resilience and Well-being
Colors can impact mood and emotional well-being:
- Color Therapy: Therapeutic approaches use colors to promote relaxation, reduce anxiety, and improve emotional resilience.
- Environmental Psychology: Studies how color in natural and built environments affects mental health and quality of life.
10. Future Directions in Color Research
Continued research explores new applications and insights into color psychology:
- Digital Environments: How colors in digital interfaces and virtual environments impact user experience and interaction.
- Health and Wellness: Exploring therapeutic uses of color in healthcare, mental health treatment, and well-being interventions.

Conclusion
Color psychology reveals the intricate ways in which colors influence human emotions, behaviors, and cognitive processes. Understanding the psychological impact of colors enables us to harness their power in various contexts—from design and marketing to healthcare and personal well-being. By leveraging the principles of color psychology, individuals and organizations can create environments that promote positivity, enhance productivity, and foster emotional well-being in an increasingly colorful world.
In Summary
Color psychology explores how different colors evoke specific emotional responses and influence human behavior. Warm colors like red and orange energize and stimulate, while cool colors such as blue and green calm and soothe. Neutral colors convey simplicity and balance. Colors play a crucial role in design, marketing, and healthcare, impacting mood, decision-making, and consumer behavior. Understanding cultural nuances and individual preferences enhances the effectiveness of color choices in creating environments that promote well-being and enhance quality of life.

