Autonomous vehicles, commonly known as self-driving cars, are poised to revolutionize the transportation industry by enhancing safety, efficiency, and convenience. Leveraging advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and sensor technologies, autonomous vehicles are set to transform how we travel and interact with our surroundings. This article explores the fundamentals of autonomous vehicles, their benefits and challenges, current developments, and the future outlook.
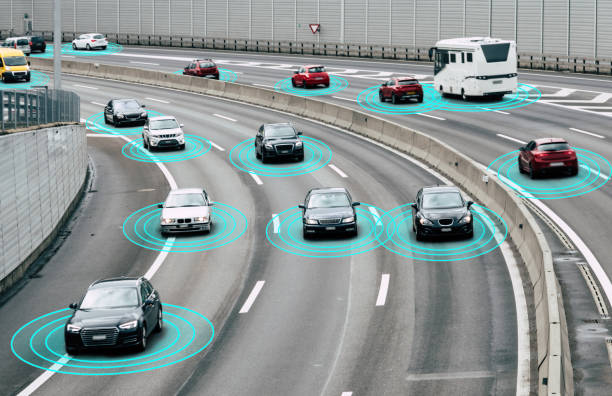
Understanding Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles are equipped with advanced technologies that enable them to operate without human intervention. These vehicles rely on a combination of sensors, cameras, radar, and AI algorithms to navigate and make driving decisions. The primary levels of autonomy, as defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), include:
- Level 0 (No Automation): The vehicle requires full human control, with no automated features.
- Level 1 (Driver Assistance): Basic automation features, such as adaptive cruise control or lane-keeping assistance, support the driver but do not replace human control.
- Level 2 (Partial Automation): The vehicle can control both steering and acceleration but requires constant human supervision.
- Level 3 (Conditional Automation): The vehicle can handle all driving tasks in certain conditions, but a human driver must be ready to take over if needed.
- Level 4 (High Automation): The vehicle can operate autonomously in specific environments or conditions without human intervention.
- Level 5 (Full Automation): The vehicle is fully autonomous and does not require any human input or oversight.
Benefits of Autonomous Vehicles
- Enhanced Safety:
- Accident Reduction: Autonomous vehicles have the potential to significantly reduce traffic accidents caused by human errors, such as distracted driving, speeding, or impaired driving. By relying on advanced sensors and AI, these vehicles can detect and respond to hazards more quickly and accurately.
- Improved Reaction Time: Autonomous systems can process data from multiple sensors in real-time, allowing for faster reaction times compared to human drivers. This can lead to a decrease in collisions and improve overall road safety.
- Increased Efficiency:
- Optimized Traffic Flow: Autonomous vehicles can communicate with each other and with traffic management systems to optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and minimize delays. This can lead to smoother and more efficient transportation networks.
- Fuel Efficiency: By driving with precision and following optimal routes, autonomous vehicles can improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Smooth acceleration and braking contribute to better fuel economy and lower environmental impact.
- Enhanced Accessibility:
- Mobility for All: Autonomous vehicles offer increased mobility for individuals who are unable to drive, such as the elderly or disabled. By providing safe and reliable transportation options, these vehicles can enhance independence and quality of life for many individuals.
- Reduced Transportation Costs: Autonomous vehicles can lower the cost of transportation by eliminating the need for a human driver and reducing the expenses associated with vehicle ownership.
- Convenience and Comfort:
- Reduced Stress: By taking over the driving responsibilities, autonomous vehicles can reduce the stress associated with driving, such as dealing with traffic congestion or navigating unfamiliar routes. Passengers can use their travel time for work, relaxation, or entertainment.
- Improved Parking: Autonomous vehicles can autonomously park in tight spaces or search for available parking spots, making parking more convenient and efficient.

Challenges and Considerations
- Technological Challenges:
- Sensor Limitations: While autonomous vehicles rely on sensors such as cameras, radar, and LiDAR, these technologies have limitations, such as reduced performance in adverse weather conditions or low-light environments. Ensuring reliable sensor performance in all conditions is a challenge.
- AI and Machine Learning: Developing AI algorithms that can accurately interpret complex driving scenarios and make safe decisions is a significant challenge. Continuous improvement and validation of these algorithms are necessary to ensure their reliability.
- Regulatory and Legal Issues:
- Safety Standards: Establishing and enforcing safety standards for autonomous vehicles is essential to ensure their safe operation on public roads. Governments and regulatory bodies need to develop comprehensive guidelines and standards for testing and deploying autonomous vehicles.
- Liability and Insurance: Determining liability in the event of an accident involving an autonomous vehicle poses legal and insurance challenges. Legal frameworks need to address questions of responsibility and coverage for autonomous vehicle accidents.
- Ethical and Social Implications:
- Decision-Making: Autonomous vehicles may face ethical dilemmas in decision-making, such as choosing between two harmful outcomes in an unavoidable accident. Addressing these ethical considerations and programming ethical decision-making into AI systems is complex.
- Impact on Employment: The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles may impact jobs related to driving, such as taxi drivers, truck drivers, and delivery personnel. Addressing the potential displacement of workers and providing retraining opportunities is important.
- Cybersecurity Risks:
- Data Security: Autonomous vehicles collect and transmit large amounts of data, including information about their surroundings and passenger preferences. Ensuring the security of this data and protecting it from cyberattacks is crucial.
- System Vulnerabilities: Autonomous vehicles rely on complex software and communication systems, which may be vulnerable to hacking or tampering. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures to protect against potential threats is essential.
Current Developments
- Pilot Programs and Testing: Many companies are conducting pilot programs and testing autonomous vehicles in controlled environments and real-world scenarios. These tests help refine the technology, identify potential issues, and gather data for further development.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Automakers, technology companies, and research institutions are collaborating to advance autonomous vehicle technology. Partnerships aim to leverage expertise, resources, and innovation to accelerate development and deployment.
- Legislative and Policy Initiatives: Governments and regulatory bodies are working to establish policies and regulations for autonomous vehicles. These initiatives focus on ensuring safety, addressing legal and ethical concerns, and facilitating the integration of autonomous vehicles into existing transportation systems.

Future Outlook
- Widespread Adoption: As technology advances and regulatory frameworks evolve, autonomous vehicles are expected to become more prevalent on roads. Widespread adoption may lead to significant changes in transportation infrastructure, urban planning, and mobility services.
- Integration with Smart Cities: Autonomous vehicles will play a key role in the development of smart cities, where interconnected technologies and data-driven solutions enhance urban living. Integration with smart infrastructure, such as traffic management systems and connected networks, will optimize transportation efficiency.
- Continued Innovation: Ongoing research and development will drive innovation in autonomous vehicle technology, including advancements in AI, sensor systems, and vehicle-to-vehicle communication. These innovations will further enhance the safety, efficiency, and capabilities of autonomous vehicles.
- Public Acceptance: Public acceptance and trust in autonomous vehicles will be crucial for their successful adoption. Continued education, transparency, and demonstration of the technology’s benefits will help build confidence and address concerns.
Conclusion
Autonomous vehicles represent a transformative shift in the transportation industry, offering the potential for increased safety, efficiency, and accessibility. While challenges such as technological limitations, regulatory issues, and ethical considerations remain, ongoing advancements and collaboration among stakeholders will drive the evolution of autonomous vehicles. As technology continues to progress and public acceptance grows, autonomous vehicles will play a significant role in shaping the future of transportation and mobility.